| Feb 10, 2024 |
(Nanowerk Information) Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan College have provide you with a brand new approach of rolling atomically skinny sheets of atoms into “nanoscrolls.” Their distinctive strategy makes use of transition metallic dichalcogenide sheets with a unique composition on both aspect, realizing a good roll that offers scrolls down to 5 nanometers in diameter on the middle and micrometers in size. Management over nanostructure in these scrolls guarantees new developments in catalysis and photovoltaic gadgets. |
|
The findings are revealed in ACS Nano (“Nanoscrolls of Janus Monolayer Transition Steel Dichalcogenides”). |
 |
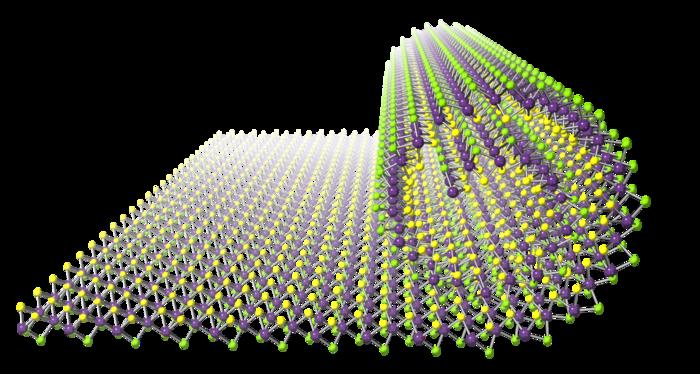
| By changing the atoms on one aspect of the nanosheet with a unique aspect, the crew have realized a nanosheet that may spontaneously roll right into a scroll when indifferent from its substrate. (Picture: Tokyo Metropolitan College) |
|
Nanotechnology is giving us new instruments to manage the construction of supplies on the nanoscale, promising a complete nano-toolset for engineers to create subsequent era supplies and gadgets. On the forefront of this motion, a crew led by Affiliate Professor Yasumitsu Miyata of Tokyo Metropolitan College have been finding out methods to manage the construction of transition metallic dichalcogenides (TMDC), a category of compounds with a variety of fascinating properties, equivalent to flexibility, superconductivity, and distinctive optical absorbance. |
|
Of their newest work, they set their sights on new methods of creating nanoscrolls, nanosheets rolled up into tight scroll-like buildings. That is a gorgeous strategy for making multi-walled buildings: for the reason that construction of every sheet is similar, the orientations of particular person layers are aligned with one another. Nevertheless, the 2 current methods of creating nanoscrolls have vital points. In a single, eradicating sulfur atoms from the floor of the nanosheet creates distortions which trigger the sheet to roll up; however by doing so, they destroy the crystal construction of the sheet. Within the different, a solvent is launched between the nanosheet and the substrate, loosening the sheet from the bottom and permitting the formation of defect-free nanoscrolls. Nevertheless, tubular buildings made like this have a tendency to have massive diameters. |
|
As an alternative of approaches like this, the crew have provide you with a brand new approach of inflicting sheets to roll up. Beginning with a monolayer molybdenum selenide nanosheet, they handled the nanosheet with a plasma and changed the selenium atoms on one aspect with sulfur; such buildings are referred to as Janus nanosheets, after the traditional two-faced god. Light addition of a solvent then loosens the sheets from the bottom, which then spontaneously roll into scrolls because of the asymmetry between the edges. |
|
These new nanoscrolls are a number of microns in size, considerably longer than beforehand made single-walled TMDC nanosheets. Moreover, they had been discovered to be extra tightly rolled than ever earlier than, with a middle down to 5 nanometers in diameter, assembly theoretical expectations. The scrolls had been additionally discovered to work together strongly with polarized mild and have hydrogen producing properties. |
|
With unprecedented management over nanostructure, the crew’s new technique kinds the muse for finding out new purposes of TMDC nanoscrolls to catalysis and photovoltaic gadgets. |