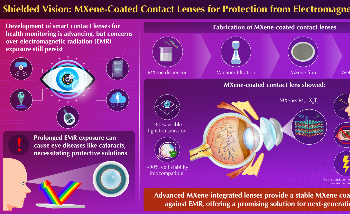
In response to a research printed in Small Science on June 4, 2025, researchers at Waseda College have developed MXene-coated contact lenses that shield the eyes from electromagnetic radiation whereas sustaining hydration and optical readability.
As sensible contact lenses change into extra frequent, issues about radiation publicity and its potential impression on eye well being are rising. These dangers embody situations resembling cataracts and different ocular illnesses. The event of MXene-coated lenses provides a possible path towards safer wearable eye applied sciences.
The rise of the Web of Issues and wi-fi gadgets has led to higher curiosity of their long-term well being results. Specifically, extended publicity to electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is a rising concern. MXenes, a category of two-dimensional transition metallic carbides and nitrides, have proven promise as supplies for EMR shielding. Nevertheless, their tendency to oxidize and poor adhesion have restricted their sensible use.
On this research, a workforce led by Professor Takeo Miyake from Waseda College’s Graduate Faculty of Info Manufacturing and Techniques in Japan developed MXene-coated contact lenses with steady optical and EMR-shielding properties. The workforce’s fabrication methodology improves the adhesion of the MXene layer and reduces oxidation, addressing key technical challenges.
The analysis was a collaborative effort between Waseda College, Kyoto College, and Yamaguchi College Hospital. The challenge mixed experience in ophthalmology, 2D supplies, and nanofabrication to make sure eye security.
Coauthors of the research embody Professor Kazuhiro Kimura and Assistant Professor Atsushige Ashimori from Yamaguchi College Hospital, Affiliate Professor Jun Hirotani from Kyoto College, Dr. Lunjie Hu from Waseda College, and Assistant Professor Saman Azhari, additionally from Waseda College.
Sensible contact lenses with built-in digital parts are getting a number of consideration as the subsequent huge factor in wearable gadgets. For the primary time, although, this implies we’ll be putting wi-fi circuit lenses straight on our corneas, exposing them to electromagnetic waves across the clock. Impressed by breakthroughs in 2D supplies and machine fabrication applied sciences, we got here up with extremely useful protecting contact lenses.
Takeo Miyake, Research Lead Creator and Professor, Waseda College
The analysis workforce started by creating MXene dispersions. These have been vacuum filtered utilizing combined cellulose ester (MCE) membranes to type MXene-based movies. A moist switch methodology utilizing acetone was then utilized to switch the movies onto industrial comfortable contact lenses.
The workforce then evaluated the bodily properties, conductivity, and security of the ensuing lenses.
“We opted for a wet-transfer methodology as a result of it permits for the straightforward attachment of MXene nanosheets to the unusually formed floor of soppy contact lenses, making certain scalability,” defined Professor Miyake.
The lenses confirmed over 80 % transmission of seen gentle, maintained conductivity, lowered dehydration, and demonstrated good biocompatibility, with greater than 90 % cell viability.
The thickness of the MXene layers various based mostly on the focus of the dispersions. The dissolved MCE membrane improved MXene adhesion and likewise helped forestall oxidation of the fabric.
Prof. Miyake discusses the importance of their methodology, saying, “Our analysis can have a multifaceted impression. First, the steady and easy coating of MXene nanosheets by way of moist switch broadens the chances for industrial functions. Secondly, our methodology is easy but efficient in stopping MXene oxidation, turning a generally ignored problem—MXene oxidation—right into a resolved impediment.”
MXene-coated lenses have been examined on porcine eyes to guage their electromagnetic shielding efficiency. The eyes have been uncovered to microwave heating and thermal imaging. The lenses confirmed a fast temperature improve, indicating efficient absorption and dissipation of electromagnetic radiation. This helped forestall direct heating of the attention tissue. Underneath high-frequency microwave publicity, the MXene materials absorbed electromagnetic vitality and launched it as thermal radiation, offering a shielding impact.
The researchers reported an electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of as much as 93 %, the best identified worth for biocompatible supplies of comparable thickness. The lenses supplied vital safety in opposition to high-frequency radiation.
These outcomes counsel that the MXene-coated lenses are a promising choice for safer wearable applied sciences. They mix electromagnetic shielding with consolation and usefulness, as a result of properties of MXene nanosheets.
Along with eye safety, this work might assist the broader use of nanomaterials in sensible wearables, medical implants, and bioelectronics, the place each security and performance are necessary.
Journal Reference:
Hu, L., et al. (2025) MXene-Built-in Contact Lens: A Breakthrough in Wearable Eye Safety and Healthcare. Small Science. doi.org/10.1002/smsc.202400628

