| Mar 02, 2024 |
(Nanowerk Information) Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan College have developed a manner so as to add single nanosheets of combined metallic oxide to gold nanoparticles supported on silica to reinforce their catalytic exercise. Changing carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide, they discovered that the temperature required for the response was drastically decreased, with vital enhancements over present strategies for coating gold/silica buildings. The strategy paves the way in which for the event of a variety of latest high-performance catalysts. |
|
The findings have been printed in ACS Utilized Supplies & Interfaces (“Ornament of Gold and Platinum Nanoparticle Catalysts by 1 nm Thick Metallic Oxide Overlayer and Its Impact on the CO Oxidation Exercise”). |
 |
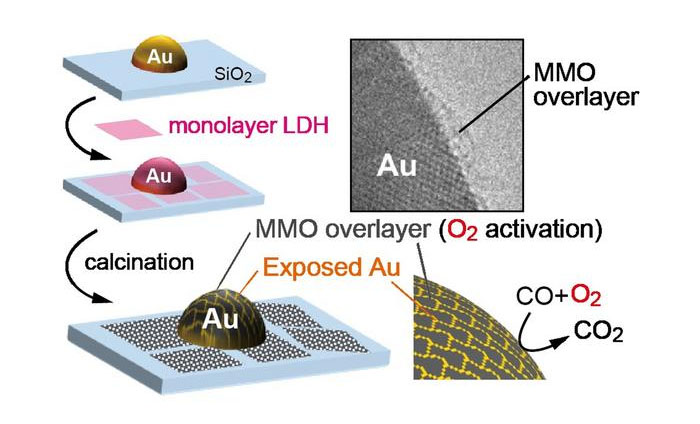
| Gold nanoparticles supported on silica are coated with monolayer LDH nanosheets and calcined to supply an ultra-thin layer of combined metallic oxide. The gold and MMO work collectively to comprehend enhanced catalytic efficiency. (inset) Transmission electron microscopy picture of the MMO overlayer. (Picture: Tokyo Metropolitan College) |
|
Gold nanoparticles, particles lower than 5 nanometers in diameter, are recognized to be glorious catalysts for chemical reactions, significantly oxidation reactions just like the conversion of dangerous carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide. The impact is pronounced when they’re mounted on metallic oxides like cobalt oxide, which usually tend to endure the alternative response i.e. reducible oxides. |
|
Sadly, not all metallic oxides are reducible. Nanoparticles mounted on irreducible oxides like silica, for instance, don’t make for an efficient catalyst. Given the abundance of silica on our planet, a manner to enhance the efficiency of such supplies would drastically increase industrial deployment. |
|
This has led scientists to look methods they will modify supported catalysts to enhance their efficiency. Now, a staff led by Affiliate Professor Tamao Ishida of Tokyo Metropolitan College have provide you with a way to deposit single nanosheets of combined metallic oxides (MMOs) utilizing layered double hydroxides (LDHs). |
|
LDHs include metallic hydroxide nanosheets with a few of the metallic ions substituted by metallic ions with the next cost, giving the sheet itself a web constructive cost; sheets are certain collectively by adverse ions. Importantly, particular person nanosheets might be exfoliated and used individually. |
|
On this research, the staff coated gold nanoparticles supported on silica, a negatively charged construction, with positively charged LDH nanosheets consisting of aluminum and a spread of different metals, then uncovered them to excessive temperatures (calcination) to type a MMO nanolayer. |
|
Observing their new catalyst utilizing transmission electron microscopy, they discovered that the nanoparticles had been coated by a layer of lower than one nanometer in thickness. To check their efficiency, the staff used them to transform carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide. |
|
Whereas gold nanoparticles on silica solely had a conversion charge of round 20% even at 300 levels Celsius, their new catalyst confirmed 50% conversion charge at solely 50 levels, a discount of greater than 250 levels. It was additionally discovered to outperform common “impregnation” strategies for MMO coating. |
|
Curiously, it was discovered that thicker MMO layers led to worse efficiency: the excessive efficiency comes from having a sub-nanometer coating. Taking a look at a cobalt aluminum MMO layer in additional element, they discovered an abundance of oxygen defects within the layer; the staff concluded that the shut synergy between this defect-filled layer and the gold floor was what gave rise to the improved exercise. |
|
The brand new catalyst realized excellent efficiency with very low ranges of cobalt inclusion, lower than 0.3percentwt. Their findings pave the way in which for utility to a variety of different supplies and a complete household of latest, high-performance catalysts. |