By design, artificial molecules usually have particular jobs to stop or speed up reactions between different molecules. To assist management extra difficult reactions, researchers might harness spare house in a single molecule to synthesize one other chemical construction. The host-guest meeting can higher induce the particular desired response than both element individually—if the scientists designing the meeting get it proper.
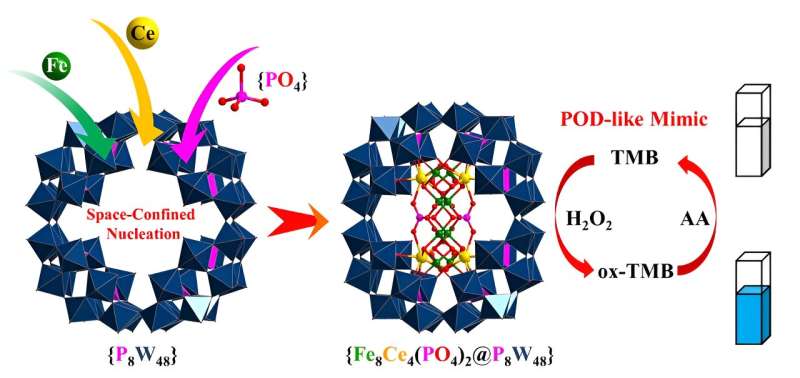
A multi-institution staff primarily based in China has reported a novel cluster—the visitor—that nucleated within a polyoxometalate (POM) nanoreactor—the host. The ensuing host-guest meeting has enhanced peroxidase-like exercise, which means it may assist speed up reactions involving the decomposition of H2O2.
These reactions are vital in organic processes, akin to defending genetic materials from oxidation injury, and have implications for superior biotechnological processes, based on the researchers.
They printed their work in Polyoxometalates.
“Some great benefits of space-confined synthesis will not be restricted to the customization of form, measurement, and composition, however of exact crystal orientation and spatial place of desired merchandise,” mentioned corresponding creator Peng Yang, professor within the Faculty of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Superior Engineering Analysis Middle of the Ministry of Training, Hunan College.
“From nanotechnology to crystal engineering, a mess of chemical forces have been employed to steer the confined development of visitor elements throughout the host containers, akin to carbon nanotubes or metal-organic framework/cages.”
The POM is a molecular framework that consists of a number of metallic ions and shared oxygen atoms with a cavity on the heart. On this cavity, researchers synthesized a novel multi-component cluster utilizing positively charged ions of iron and cerium, in addition to phosphate. The cluster nucleated, which means it fashioned a cluster with a transparent heart within the POM’s cavity.
“We discovered that novel constructions of polyoxometalates might be obtained by confining the synthons inside particular nanospaces, and the confined artificial technique excels at permitting us to make the most of these nanospaces,” Yang mentioned, explaining that synthons will not be a reagent however can sign the beginning of a reagent wanted to synthesize a goal molecule. “Inside the cavity of this polyoxometalate, we efficiently nucleated this novel cluster for the primary time.”
The researchers analyzed the cluster’s construction and composition, in addition to investigated its potential capabilities. In response to Yang, preliminary research on the POM cluster yielded promising outcomes testifying to its capacity to detect ascorbic acid—an antioxidant that helps shield cells from free oxygen that may inflect injury—with excessive sensitivity and specificity.
“This work opens up extra potentialities within the improvement of POM-based molecular assemblies from custom-made synthesis through structural design to utility enlargement,” Yang mentioned.
Extra data:
Hong-Xin Sheng et al, From confined development to enhanced peroxidase-like exercise: Nucleation of a phosphate-mediated Fe III–Ce III–oxo cluster contained in the {P 8W 48} nanoreactor, Polyoxometalates (2024). DOI: 10.26599/POM.2024.9140060
Offered by
Tsinghua College Press
Quotation:
Not only a lodger: Novel host-guest meeting supplies enhanced reactivity (2024, March 15)
retrieved 17 March 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-03-lodger-host-guest-reactivity.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.

