| Feb 22, 2024 |
(Nanowerk Information) Longstanding challenges in biomedical analysis resembling monitoring mind chemistry and monitoring the unfold of medication via the physique require a lot smaller and extra exact sensors. A brand new nanoscale sensor enormously outperforms customary applied sciences by monitoring areas 1,000 occasions smaller and monitoring refined adjustments within the chemical content material of organic tissue with sub-second decision. |
The nanosensor gadget, developed by researchers on the College of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, is silicon-based and takes benefit of strategies developed for microelectronics manufacturing. The small gadget measurement allows it to gather chemical content material with near 100% effectivity from
extremely localized areas of tissue in a fraction of a second. The capabilities of this new nanodialysis gadget are reported within the journal ACS Nano (“Extremely localized chemical sampling at sub-second temporal decision enabled with a silicon nanodialysis platform at exceedingly sluggish flows”). |
 |
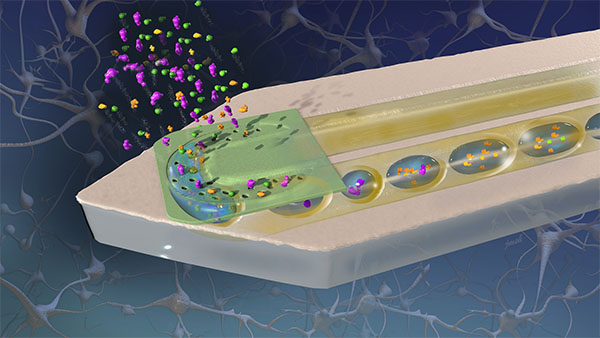
| Illustration of the nanosensor’s operation. (Picture: Holonyak Micro & Nanotechnology Lab) |
“With our nanodialysis gadget, we take a longtime approach and push it into a brand new excessive, making biomedical analysis issues that have been unimaginable earlier than fairly possible now,” stated Yurii Vlasov, a U. of I. electrical & laptop engineering professor and a co-lead of the research.
“Furthermore, since our units are made on silicon utilizing microelectronics fabrication strategies, they are often manufactured and deployed on massive scales.” |
From micro- to nanodialysis |
|
Nanodialysis is predicated on a way known as microdialysis wherein a probe with a skinny membrane is inserted into organic tissue. Chemical substances cross via the membrane right into a fluid that’s pumped away for evaluation. The power to immediately pattern from tissue has made a serious affect in fields like neuroscience, pharmacology and dermatology. |
Conventional microdialysis has limitations, although. The probes pattern from a couple of sq.
millimeters, to allow them to solely measure the typical composition over comparatively massive areas within the tissue. The big measurement additionally leads to some extent of tissue injury when the probe is inserted, probably skewing the evaluation outcomes. Lastly, the fluid pumped via the probe flows at a relatively excessive fee, impacting the effectivity and accuracy with which chemical concentrations could be learn. |
|
“Many issues with conventional microdialysis could be solved by utilizing a a lot smaller gadget,” Vlasov stated. “Going smaller with nanodialysis means extra precision, much less injury from the tissue placement, chemically mapping the tissue with increased spatial decision, and a a lot sooner readout time permitting a extra detailed image of the adjustments in tissue chemistry.” |
 |
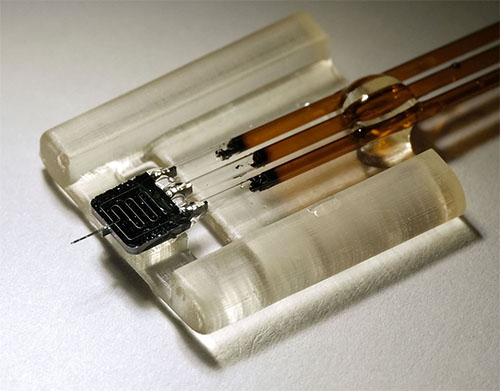
| The fabricated and packaged nanodialysis gadget. (Picture: Holonyak Micro & Nanotechnology Lab) |
Gradual and regular |
An important function of nanodialysis is the ultra-slow stream fee of the fluid pumped
via the probe. By making the stream fee 1,000 occasions slower than conventional microdialysis, the gadget captures the chemical composition of the tissue collected from an space 1,000 occasions smaller than conventional strategies whereas sustaining 100% effectivity. |
|
“By drastically lowering the stream fee, it permits the chemical compounds diffusing into the probe to match the concentrations outdoors within the tissue,” Vlasov defined. “Think about you’re including dye to a pipe with flowing water. If the stream is just too quick, the dye will get diluted to concentrations which are tough to detect. To keep away from dilution, you might want to flip the water nearly all the best way down.” |
Silicon fabrication and manufacturing |
|
Commonplace microdialysis units are constructed utilizing glass probes and polymer membranes, making them a problem to miniaturize. To construct units appropriate for nanodialysis, the researchers used strategies developed for digital chip manufacturing to create a tool primarily based on silicon. |
|
“Along with enabling us to go smaller, silicon know-how makes the units cheaper,” Vlasov stated. “By placing within the effort and time to develop a fabrication course of for constructing our nanodevices on silicon, it’s now very simple to fabricate them at industrial scales at an extremely low value.” |