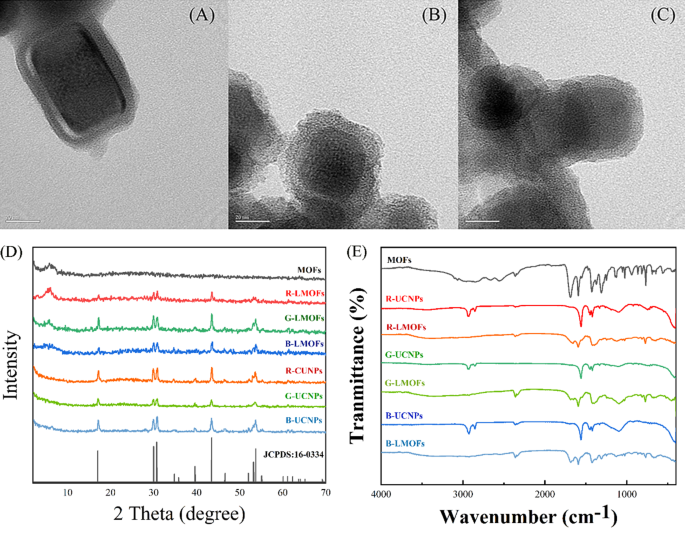
Characterization of LMOFs
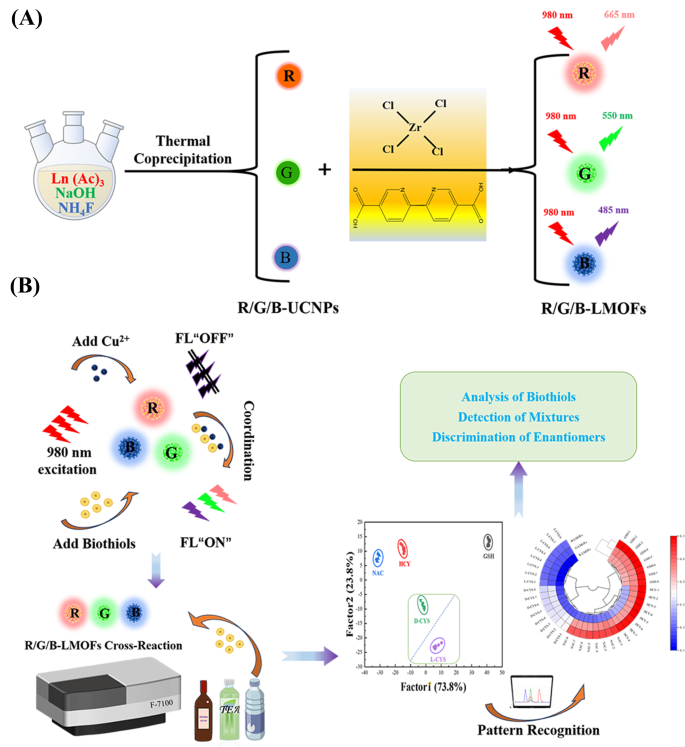
As a way to realise the facile evaluation for biothiols, a tricolor upconversion fluorescence sensor array based mostly on R/G/B-LMOFs was additional developed. The core − shell construction R/G/B-LMOFs supplies have been designed and synthesised by introducing MOFs cladding layer onto the floor of the corresponding R/G/B-UCNPs in a facile technique, the place zirconium (IV)-based UiO-type MOFs bridged by BPy-DCA ligands was in situ paved with R/G/B-UCNPs by self-assembly pushed by electrostatic interplay (Scheme 1A). The obtained three LMOFs supplies have been additional analysed to evaluate their elemental composition, morphology, XRD, FT-IR, UV-Vis, TGA and fluorescence traits. The corresponding primary elemental composition within the ensuing R-UCNPs (Y, Tm and Er), G-UCNPs (Y, Yb and Er), B-UCNPs (Y, Yb and Tm), R-LMOFs (Zr, Y, Tm and Er), G-LMOFs (Zr, Y, Yb and Er), and B-LMOFs (Zr, Y, Yb and Tm) have been noticed (Fig. S1), which confirmed that Zr (IV)-based MOFs have been efficiently assembled with the corresponding UCNPs, respectively. The SEM picture of the ensuing R/G/B-LMOFs exhibited the same agglomerated granular construction with MOFs (Fig. S2), and the TEM morphology of R/G/B-LMOFs revealed the same core − shell construction with common measurement about 40–50 nm, whereby the MOFs layer (about 7 nm thick) was assembled onto the hexagonal part R/G/B-UCNPs (about 30–40 nm) (Fig. 1A and C and Fig. S3), which indicated that the core − shell construction R/G/B-LMOFs supplies have been efficiently synthesized. The investigation of crystal construction revealed that the diffraction peaks of the ensuing R/G/B-LMOFs built-in the attribute peaks of pure MOFs and the corresponding R/G/B-UCNPs outfitted with the pure hexagonal part of NaYF4 (JCPDS no. 16–0334) (Fig. 1D). The corresponding useful group data of R/G/B-LMOFs in FT-IR spectroscopy confirmed that the seen attribute stretching vibrations peaks of R/G/B-LMOFs have been just like the pure MOFs. The rising attribute peak (1659, 1668, and 1682 cm− 1) have been related to the C-N stretching frequency of pyridine teams on R/G/B-LMOFs in contrast with R/G/B-UCNPs (Fig. 1E), which indicated that the MOFs layer was lined onto the floor of UCNPs. In the meantime, TGA revealed that every one the three R/G/B-LMOFs have good thermal stability (Fig. S4).
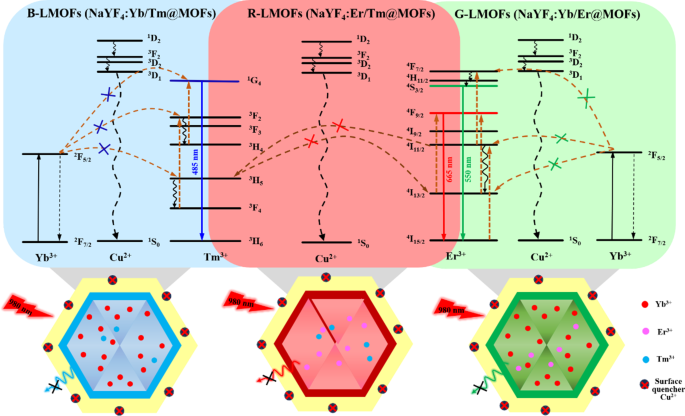
The fluorescence emission spectra of the obtained R/G/B-LMOFs supplies have been measured below an excitation wavelength of 980 nm (Fig. S5), which exhibited the attribute spectra of the corresponding core R/G/B-UCNPs as a result of photon vitality degree transition and vitality switch of the completely different doping parts in UCNPs, the place the principle pink emission (665 nm) of R-UCNPs (NaYF4:Er/Tm) is comparable to 4F9/2→4I15/2 transitions of Er3+ within the vitality switch between Er3+ and Tm3+, the principle inexperienced emission (550 nm) of G-UCNPs (NaYF4:Yb/Er) is comparable to 4S3/2→4I15/2 transitions of Er3+ within the vitality switch between Yb3+ and Er3+, and the principle blue emission (485 nm) of B-UCNPs (NaYF4:Yb/Tm) is comparable to 1G4→3H6 transitions of Tm3+ within the vitality switch between Yb3+ and Tm3+. In the meantime, the fluorescence emission depth of R/G/B-LMOFs have been stronger than that of the corresponding core R/G/B-UCNPs, which may very well be resulted from that the inert MOF shell adjusted the lattice defects on the floor of the core UCNPs and/or the inert MOF shell served as a spacer matrix to isolate the quenching impact of solvent molecules [6]. The quantum yield and fluorescence lifetime investigation additional confirmed the wonderful optical properties of R/G/B-LMOFs (Desk S1). These outcomes demonstrated that the R/G/B-LMOFs-based sensors might present glorious upconversion luminescence properties and ample bipyridine useful websites within the fluorescence sensing.
Fluorescence response mechanism of LMOFs
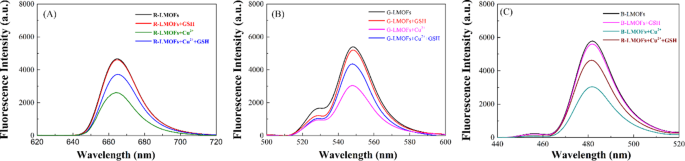
Typically, the bipyridine teams can coordinate selectively with Cu2+, which might reinforce the interplay of LMOFs to Cu2+ than that of the core UCNPs to Cu2+. As anticipated, three R/G/B-LMOFs revealed extra stronger fluorescence quenching to Cu2+ than that of the corresponding core R/G/B-UCNPs as a result of introduction of MOFs with bipyridine teams to UCNPs (Fig. S6). The fluorescence response mechanism of LMOFs to Cu2+ was additional explored. The looks of a small blue shift in UV-Vis spectrum was ensuing from the interplay between R/G/B-LMOFs and Cu2+, which preliminary implied the formation of cupric bipyridine coordinates (Fig. S7). The absorption band that resulted from the interplay of Cu2+ with MOFs aren’t overlapped with the fluorescence emission peaks of R/G/B-LMOFs, which could be inferred that the Cu2+-induced fluorescence quenching of R/G/B-LMOFs may very well be attributable to the vitality switch somewhat than the inner-filter impact (Fig. S8). Impressed by earlier research, the potential vitality switch mechanism concerning the Cu2+-induced fluorescence quenching of R/G/B-LMOFs was proven in Fig. 2, whereby the vitality switch mechanism of Er3+, Tm3+, and Yb3+-assisted upconversion course of within the NaYF4 below excitation of 980 nm may very well be disturbed by Cu2+. Because of the potential overlap between lanthanide metallic ions-trimer luminescence peak with the absorption spectrum of cupric bipyridine coordinates, the current Cu2+ on the floor of LMOFs might disturb the vitality switch from Er3+ to Tm3+(R-LMOFs), Yb3+ to Er3+(G-LMOFs), and Yb3+ to Tm3+(B-LMOFs), and the corresponding vitality switch was transferred to the 1D2 degree of Cu2+, forming the non-radiative transition from the de-excitation of Cu2+ to the bottom state [28]. Such outcomes supported the vitality switch mechanism in LMOFs-based sensing system for Cu2+. In the meantime, R/G/B-LMOFs confirmed apparent fluorescence response to Cu2+ than that of different divalent metallic ions and biomolecules (Fig. S9). After optimizing the sensing situations (Fig. S10), the fluorescence depth of all of the three R/G/B-LMOFs progressively decreased with the growing of Cu2+ (5.0 × 10-8-1.0 × 10− 6 M) and the plots of the fluorescence quenching diploma ((F0-Fi)/F0) versus Cu2+ exhibited a superb linear correlation, which additionally exhibited a sure of fluorescence response distinction between the three R/G/B-LMOFs to Cu2+ (Fig. S11). Herein, we speculated that the fluorescence response of R/G/B-LMOFs to Cu2+ may very well be disturbed by some targets that may mix with Cu2+, and their fluorescence response distinction may very well be enlarged to kind the distinctive fluorescence fingerprint of the targets. Impressed by the simple coordination of Cu2+ with sulfhydryl teams, biothiols have been launched into the sensing platform of LMOFs and Cu2+ to confirm the speculation. GSH was chosen as mannequin biothiols to discover the fluorescence response mechanism within the sensing platform of R/G/B-LMOFs and Cu2+. All of the three R/G/B-LMOFs exhibited apparent fluorescence quenching to Cu2+, whereas little fluorescence response to GSH. As anticipated, the launched GSH can affect the fluorescence quenching of R/G/B-LMOFs triggered by Cu2+ as a result of aggressive binding between GSH with Cu2+ (Fig. 3). Below the optimum working situations (Fig. S12), the fluorescence depth of R/G/B-LMOFs elevated with the rise of GSH content material (5.0 × 10-5-1.0 × 10− 7 M) and the plot of fluorescence response ((Fi-F0)/F0) versus the logarithm of GSH focus confirmed a superb linear relationship (Fig. S13). The fluorescence response within the three R/G/B-LMOFs may very well be employed because the distinctive fingerprint of GSH, and the popularity fingerprint of different biothiols may very well be additional obtained from the sensing platforms.
Sample recognition of biothiols utilizing R/G/B-LMOFs fluorescence sensor array
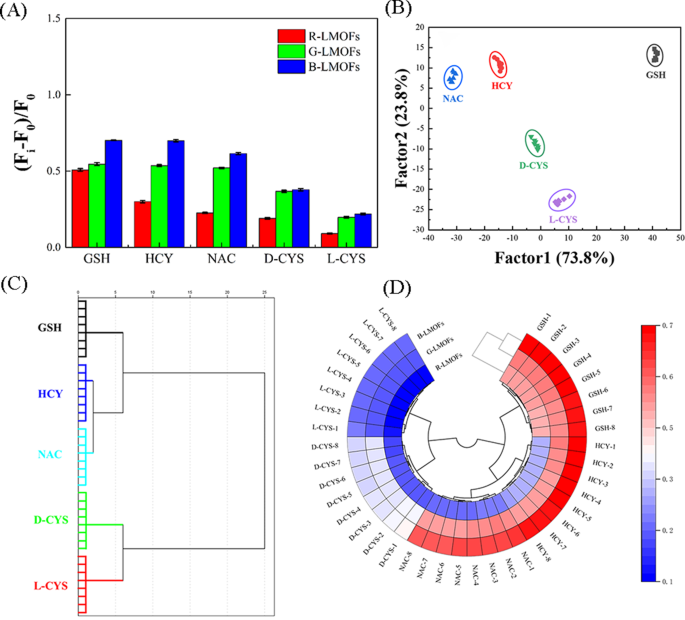
By advantage of the near-infrared characteristic and glorious responsiveness, three R/G/B-LMOFs have been employed to assemble a tricolor upconversion fluorescence sensor array for the sample recognition of 5 biothiols (together with GSH, HCY, NAC, and D/L-CYS) (Desk S2), whereby every R/G/B-LMOFs might reply to biothiols and the traits of every biothiols may very well be mirrored by the generated options fluorescence sign from the cross-reactive of R/G/B-LMOFs in a novel method (Scheme 1B). Below the optimum working situations, 5 biothiols have been detected within the R/G/B-LMOFs fluorescence sensor array, three R/G/B-LMOFs confirmed vital fluorescence response ((Fi-F0)/F0) towards 5 sorts of biothiols (100 µM), which was common and carefully associated to biothiols (Fig. 4A). The obtained fluorescence indicators have been additional skilled in a matrix (R/G/B-LMOFs × 5 biothiols × 8 replicates) to maximise the separation capacity because the “identification fingerprints” of biothiols through the use of LDA, which could be employed to categorise, separate, and determine biothiols with the linear mixture of options by changing the coaching matrix into canonical scores in response to Mahalanobis distance. The generated three canonical elements (73.8%, 23.8% and a couple of.4%) for the full variance have been plotted into the 2D determine, the place every form of biothiols was well-clustered with none overlap, discriminating totally from one another (100% accuracy) (Fig. 4B). In the meantime, the dendrogram of 5 biothiols have been clustered independently in response to the classes by HCA (Fig. 4C), and the distinction amongst 5 biothiols within the three R/G/B-LMOFs channels additionally was displayed by the warmth mapping (Fig. 4D), which revealed the great potential of the R/G/B-LMOFs fluorescence sensor array in distinguishing biothiols. Inspired by such outcomes, the R/G/B-LMOFs fluorescence sensor array was additional employed to confirm the popularity capacity of 5 biothiols at a decrease focus (50 µM), and the outcomes of LDA, HCA and heatmapping demonstrated a greater sample recognition with excessive accuracy in the direction of the low focus biothiols (Fig. S14 and S15), which displayed the next sensitivity over the earlier report (100 µM) [29, 30]. Delightedly, we discovered that the 2 chiral enantiomers biothiols (L-Cys and D-Cys) have been impartial of one another within the LDA, HCA and heatmapping, which was highlighting the capability for chiral recognition.
(A) Sign patterns of the relative fluorescence selection ((Fi-F0)/F0) of the R/G/B-LMOFs fluorescence sensor array within the presence of 5 biothiols (100 µM). (B) Canonical rating plot of 2D for the response patterns of biothiols obtained from LDA. Every level represents the response sample for single biothiols species. (C) Dendrogram generated by HCA of 5 biothiols, and (D) Ring warmth mapping of 5 biothiols
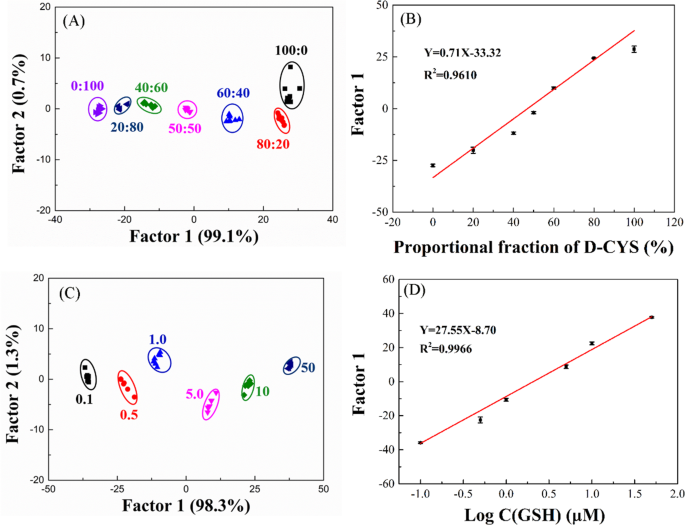
To additional discover the efficiency of the R/G/B-LMOFs fluorescent sensor array, the completely different molar ratios of L-Cys and D-Cys mixtures could be totally distinguished by the R/G/B-LMOFs fluorescence sensor array and the obtained first discriminant Issue 1 values fluctuate with the proportion of the 2 L/D-Cys (Fig. 5A and B), which was cost-effective and simple to make use of than that of the standard chromatographic strategies. In the meantime, the completely different focus of GSH could be separated in LDA rating plot (Fig. 5C), and the primary discriminant Issue 1 values have been linearly associated to the logarithm of the concentrations of GSH (Fig. 5D), and the same evaluation outcomes could be discovered within the different biothiols (NAC, HCY, and L/D-CYS) (Fig. S16), which demonstrated the feasibility of the proposeded fluorescence sensor array within the quantitative evaluation.
(A) Canonical rating plot towards the mixtures of L-CYS and D-CYS by LDA. (B) Variation curve of Issue 1 values and the combination of L-CYS and D-CYS. (C) Canonical rating plot towards completely different concentrations of GSH by LDA. (D) The linear becoming curve representing relationship between the completely different concentrations of GSH and Issue 1 values
Identification of biothiols in actual samples
The sensible utility of the proposed R/G/B-LMOFs fluorescence sensor array was additional investigated in tea beverage and white wine samples. Customary addition technique was employed by spiking recognized quantities of biothiols (100 µM) into samples extraction, and 30 unknown biothiols have been spiked in tea drink and white wine samples respectively and randomly picked from the matrix (Desk S3–S6). The blind checks exhibited 90.0% accuracy in biothiols discrimination and the outcomes have been dependable in tea drink with 93.3% accuracy, which is increased than that of white wine (86.7%) (Desk 1), which indicated the great sensible functions potential of the developed fluorescent sensor array for biothiols detection.